Engineered resilience-pioneer of resilience theory in ecology (stable design parameter of technologies)
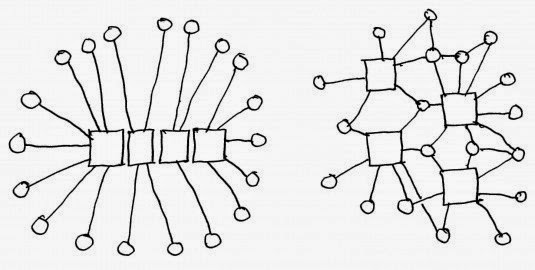
Left:
over-concentration of large-scale components;
Right: more resilient
distributed network of nodes
1.
Fukushima: nuclear reactor group in
Japan.
X ecological resilience (the
resilience to the often-chaotic disruptions[earthquake & tsunami] that
ecological systems have to endure)
2. Humans
are contributing to the instability (in the form of increasingly complex technology
and its unpredictable interactions and disruptions).
3. Effect:
climate change, complex & unstable infrastructures in vulnerable coastal
locations
4.
Rainforest: generates complicated interactions yet manage to remain stable, in
spite of countless disruptions and “shocks to the systems”.
1) These systems
have an inter-connected network structure.
2) They feature
diversity and redundancy (a totally distinct notion of
“efficiency”).
3) They display a
wide distribution of structures across scales, including fine-grained scales.
4) They
have the capacity to self-adapt and “self-organize.” This
generally (though not always) is achieved through the use of genetic
information.
0 Comments:
Post a Comment
『卻說不出在什麽場合我曾讓你分心。
你離開我,這是旅行的意義』